The 30-Minute Technical SEO Audit Anyone Can Do [Updated]
Author’s Note: We’ve given this blog post a refresh on November 2, 2023, complete with fresh information, new links, relevant data, and more.
In the last article, we talked to about technical SEO and what it entails.
In this article, we’ll talk about how to conduct a technical SEO audit. What to look for? What tools to use? And what to focus on?
In this post, we’ll cover the following:
- Selecting Your SEO Tools
- What to Focus on First
- Page Speed
- Mobile Accessibility & Core Web Vitals
- Deepening Your Technical SEO Understanding
- Key Takeaways
Selecting Your SEO Tools
Unless your website has less than 50 pages or so, you’re going to need an SEO auditing tool to crawl the website. The most popular SEO auditing software tools are SEMrush, ahrefs, and ScreamingFrog.
Personally, SEMrush is my favorite because they grade your overall site health and provide a comprehensive user-interface for reporting, keyword tracking, and a lot of other features.
Ahrefs is great for backlink auditing, building backlinks, and anything that has to do with the back links. But it is not ideal for auditing websites.
ScreamingFrog is a great tool and I will sometimes run it in parallel alongside SEMRush. It’s also significantly cheaper than both SEMrush and ahrefs, probably because there is no user interface in the cloud. It’s great to crawl the website and export that data to Google Sheets or Excel but there isn’t a user interface that allows you to run reports and present to clients.
Google Search Console and Google Analytics are also tools that you will want to have set up and connected so that you can accurately track your organic traffic.
For the purpose of this article, I will be using SEMrush and a few other tools for specific things such as site speed.
What to Focus on First
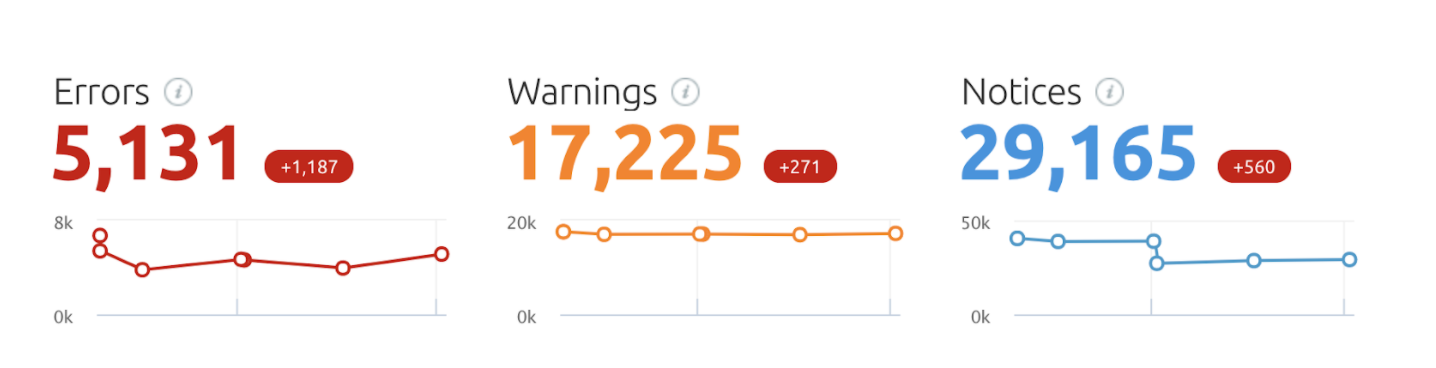
Another reason why I like SEMrush is that it prioritizes the most important errors, warnings, and notices.
- Errors are issues of the highest severity and should be fixed first.
- Warnings aren’t as important but you should attempt to fix as many as possible.
- Notices are not so important and most likely will not be fixed on larger sites.
These errors may look alarming but it’s important to understand that you’re not going to be fixing every single one. The audit takes into account SEO best practices and this would be the ideal if you are 100% focused on SEO and we’re willing to potentially compromise other aspects of the website to fix all SEO notices. So let’s drill down into the errors and see what to fix first.
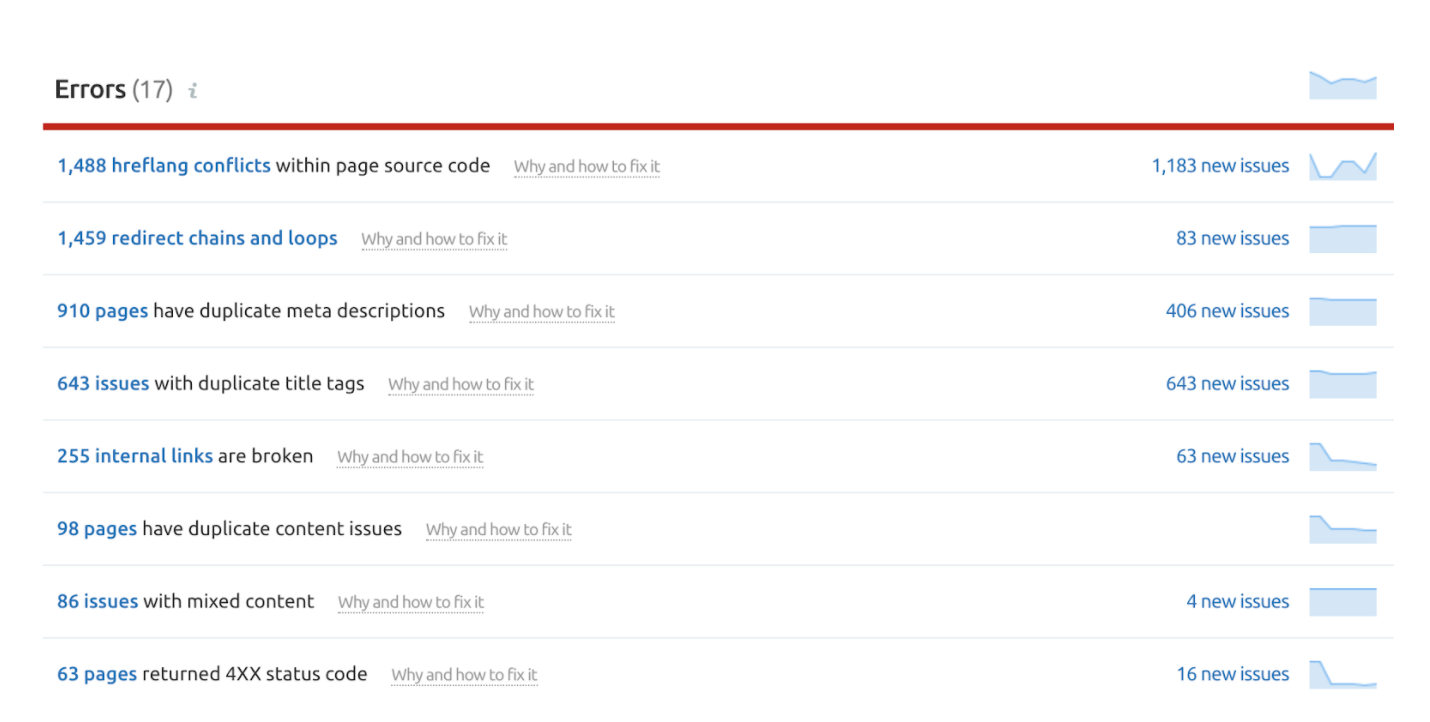
The above screenshot shows the eight most critical errors that we must fix. You can click on each one and drill down to see exactly which pages the errors occur on. They also do a great job of explaining what the error is and how to fix it.
Since we have to fix them all we have to decide which one to start with. The easy thing to do is look at which one has the most errors and start there – hreflang conflicts. Another reason why this is a good error to start with is that it can be fixed programmatically. With a few lines of code, we can fix all 1400+ hreflang errors in the span of a few hours.
This is just a personal preference, but it’s always great to come back to your client and say “hey look, we fixed 1400 errors in our first week of implementing SEO fixes”. It’s a quick win and it goes a long way rather than starting with the 900 duplicate meta descriptions, which may take weeks to completely finish and deliver to the client.
After fixing all of the errors to the best of our ability we would then go on and do the same with the warnings and then the notices. My personal goal is to get the site health to 90%. That tends to be very challenging with large websites.
Page Speed
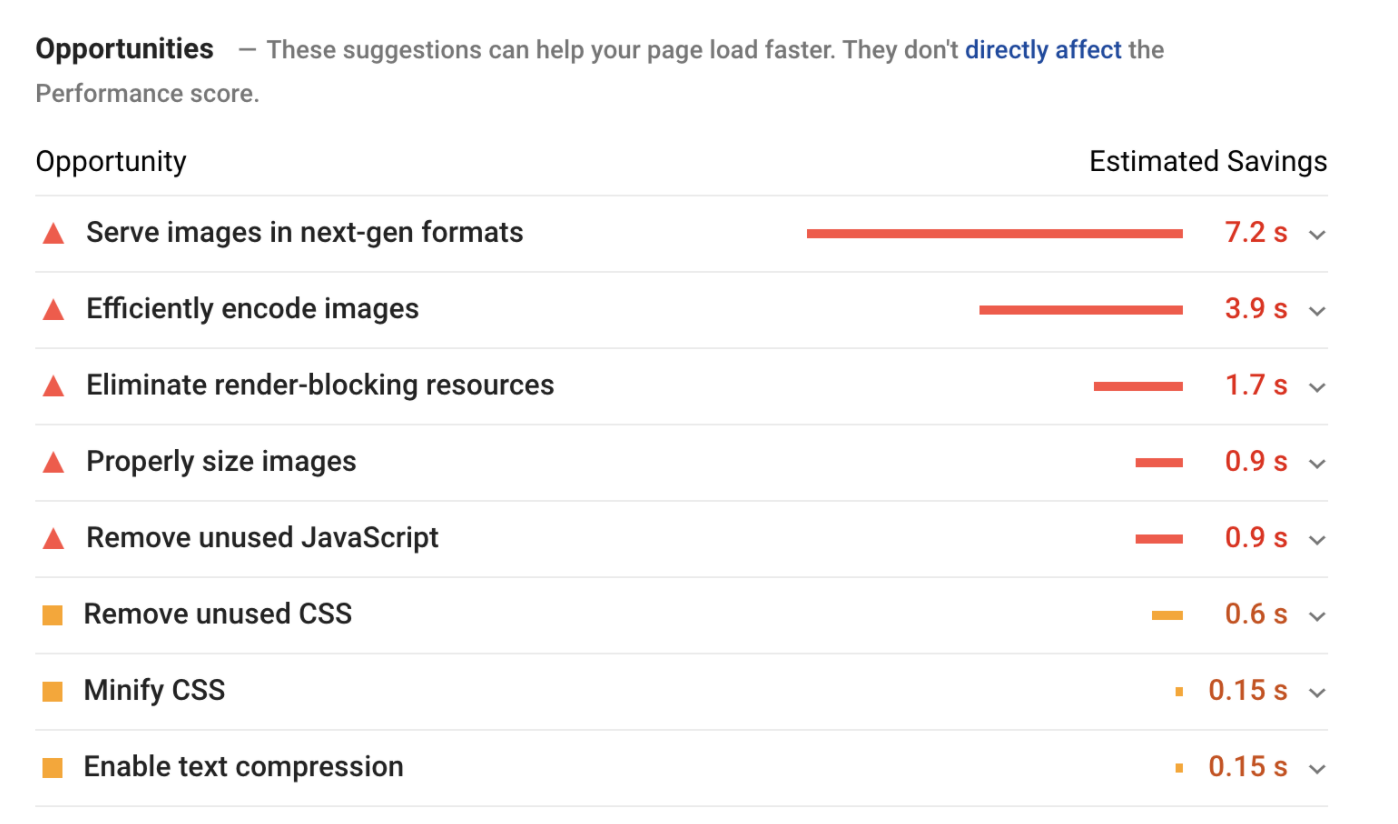
With page speed being so important, there are a dozen different tools we could use to check our page speed. We’re going to rely on the ones that are provided by Google today, specifically Google pagespeed insights.
Focusing on the opportunities, we can see that images are significantly slowing down this particular website. So we would click on the errors and find solutions to the problems and present them to the client.
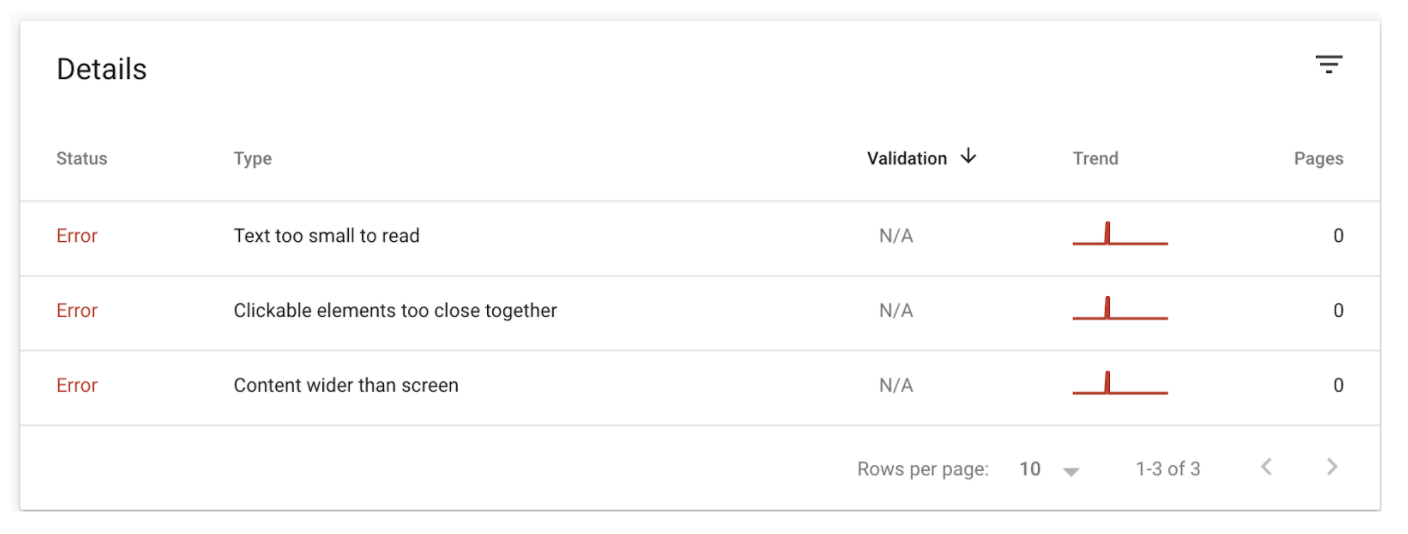
Mobile Accessibility & Core Web Vitals
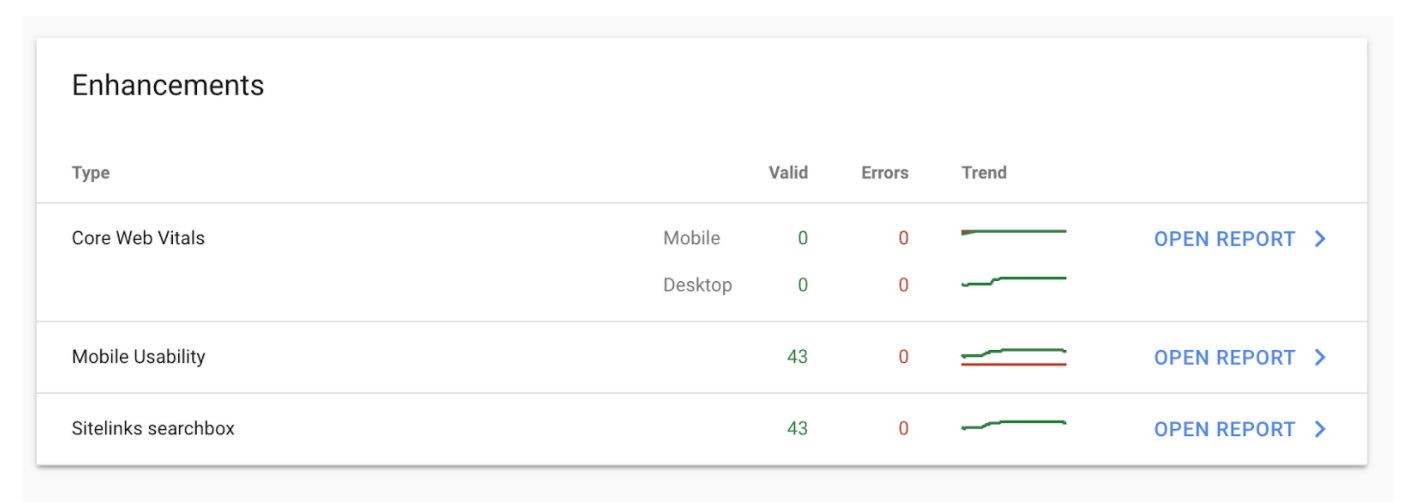
The rest of the technical SEO aspects that we’re going to look at today can all be viewed from Google Search Console.
Fortunately, this particular website doesn’t have any errors but if it did we would click on open report, find the specific hour, and go in and fix it.
This usually requires working closely with the developer as you can see most of the errors revolve around coding. This is also the same for the core web vitals, which mainly focuses on the speed of the website on desktop and mobile.
Deepening Your Technical SEO Understanding
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of SEO, it’s essential to have a firm grasp on several core components that significantly impact your site’s performance and search engine ranking. The following sections will provide insights and actionable steps to analyze and optimize your site’s indexation, canonicalization, XML sitemaps, robots.txt file, structured data, site architecture, server performance, and security protocols. Each of these elements plays a pivotal role in ensuring your website is well-optimized, secure, and user-friendly, contributing to an enhanced online presence and better SEO results.
Indexation Analysis
Ensuring the right pages are indexed is foundational in a technical SEO audit. Utilize Google Search Console to check the Index Coverage report, identifying any pages that are excluded or have warnings. For a finer granularity, use the site:operator on Google Search along with your domain to see exactly what’s indexed. It’s advisable to also check for unwanted pages in the index and apply the “noindex” tag accordingly.
Canonicalization
Proper implementation of canonical tags is vital to prevent duplicate content issues which could dilute your site’s SEO value. Check for correct canonical tag implementation using tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb. They provide data on pages with missing or incorrect canonical tags. Establish a protocol for canonicalization, ensuring that every new page has a correct canonical tag pointing to its preferred version.
XML Sitemaps
An accurate and comprehensive XML sitemap guides search engines to the important pages on your site. Use tools like SEMrush or Screaming Frog to audit your sitemap for errors or omissions. Ensure that your sitemap is updated regularly, especially after adding or removing pages. Submit your sitemap via Google Search Console and monitor the Sitemaps report to ensure that your pages are being discovered and indexed properly.
Robots.txt
Analyzing the robots.txt file is crucial as it directs search engine bots on which pages to crawl and index. A well-configured robots.txt file ensures that search engines can access essential content while avoiding less important or sensitive areas of your site. Utilize tools like Google’s Robots Testing Tool to analyze the directives in your robots.txt file, ensuring they align with your indexing goals. By reviewing and testing your robots.txt file regularly, you can maintain optimal crawl efficiency and ensure that search engines are accessing the right content.
Structured Data
Verifying the implementation of schema markup is essential to enhance your site’s appearance in SERPs. Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool can be invaluable for checking your markup for errors or omissions.
But with the recent changes to Google’s algorithms, first you want to evaluate just how helpful structured data will be for your website and industry. For instance, event structured data is no longer showing in SERPs but eCommerce product and review schemas can still significantly enhance your product listings in SERPs.
Site Architecture
A well-organized site architecture is like having a well-laid out map for both your visitors and search engines.
- URL Structure: Descriptive URLs: Ensure URLs succinctly describe the content on the page.
- URL Length: Keep URLs short yet descriptive; it’s recommended to stay under 60 characters.
Internal Linking
- Link Relevancy: Ensure that links are relevant to the context of the page.
- Anchor Text: Use descriptive anchor text to improve user experience and SEO.
Site Navigation
- Breadcrumbs: Implement breadcrumbs to help users navigate your site.
- Navigation Menu: Maintain a clean, easy-to-understand navigation menu.
By optimizing these aspects, you create a favorable environment for search engines to crawl and index your content efficiently, and for users to navigate your site effortlessly.
Server Performance
Evaluating server performance is like ensuring the engine of your website is running smoothly. Here’s a breakdown to assist you in diving deeper:
Response Codes
- Error Codes: Look out for 4xx and 5xx error codes that indicate client and server errors respectively.
Redirects
- Redirect Chains: Identify and fix redirect chains which could slow down page loading times.
Performance Testing
- Load Time: Tools like GTmetrix or Pingdom provide insights into server performance and potential bottlenecks.
Optimization
- Caching: Implement server caching to improve load speed.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Utilize a CDN to distribute the load, saving bandwidth and speeding up access for your users.
Regular Audits
- Monitoring Tools: Employ monitoring tools to get real-time insights and historical data on your server performance.
Hosting Environment
- Server Type: Ensure your hosting environment is adequately configured and optimized for performance. By taking these steps, you’ll be on a good path to optimizing your server performance, enhancing site speed, and providing a better user experience.
Security Audit (HTTPS Issues)
Conducting a security audit to identify HTTPS issues is fundamental to ensure the protection of your site’s data and build trust with your visitors. Utilizing tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Server Test can provide a comprehensive review of your site’s SSL/TLS configuration and highlight areas for improvement.
Key Takeaways
Conducting a technical SEO audit is an imperative step to uncover the strengths and weaknesses of your website from an SEO standpoint. Through the use of various tools like SEMrush for a comprehensive SEO audit, URL inspection tools for evaluating URL structure, and Google’s robots.txt Testing Tool for analyzing directives, you can garner a plethora of insights.
This audit helps in optimizing internal and external links, ensuring a well-laid architecture, and enhancing server performance for a swift user experience. The ultimate goal is to improve your site’s visibility in search results, making it easily accessible to both users and search engine crawlers. This meticulous process, although time-consuming, is a cornerstone for achieving better SEO results and a more robust online presence. If you are not experienced with this then I recommend hiring a technical SEO agency to take care of it for you.

Derek is a digital marketer based in Boston, Massachusetts with almost a decade of hands-on SEO experience. He finds it meaningful, challenging, and exciting to develop, test, and implement new SEO strategies. When he’s not auditing websites and optimizing content he’s usually backpacking and exploring new cultures.