Duplicate Content and SEO Guide
When conducting technical SEO audits, one of the most common errors that I see on sites is duplicate content. It is also one of the most important issues to fix because it can hurt your chances of growing your site organically.
Luckily, with a basic understanding of what duplicate content is, what it means for your site’s SEO, and how to identify and fix it, dealing with it will seem less daunting.
Table of contents:
- What is duplicate content in SEO?
- Why is having duplicate content bad for SEO?
- How to spot duplicate content
- Examples
- How to fix duplicate content
What is duplicate content in SEO?
Duplicate content is when you have similar or the same content on different pages of your site.
The definition of duplicate content might seem self-explanatory. However, in practice, the reason your site is flagged for duplicate content and the solution to fix it varies greatly. Therefore, it can be complex for someone that is not familiar with duplicate content or SEO.
Why is having duplicate content bad for SEO?
“Why does it matter if we have duplicate content?” I’ve heard variations of this question from several clients. Duplicate content negatively affects your SEO in four main ways.
- Site health
- Organic performance and rankings
- Crawling and indexing
- User experience
No matter what is causing the duplicate content issue on your site, the issue itself greatly impacts your health and performance because it confuses search engines.
When you have similar or duplicate pages, Google doesn’t know which URL or version of a page to index. As a result, you could end up not ranking for anything or not appearing in the search results at all. Not to mention, you could be wasting your crawl budget on duplicate pages.
Lastly, if you have multiple URLs that have similar or identical content it can also negatively impact your user experience.
Is there a duplicate content penalty?
You may hear the term “duplicate content penalty” thrown around. Google does not have an official duplicate content penalty. However, many sites experience ranking and health issues because of duplicate content.
Site health scores also tend to increase—sometimes by as much as ten points or more—after fixing duplicate content SEO issues. I’ve seen sites that were struggling to rank for keywords or had wild fluctuations begin to steady and rank on the first page of search results.
Duplicate content happens for a variety of reasons, and it’s not usually as simple as “there’s the same content on different pages”. Most of the time, it requires technical SEO fixes.
The first step to fixing duplicate content is to identify where it is on your site and why it’s happening.
How to spot duplicate content
To identify duplicate content, you can use an SEO auditing tool like Semrush or Ahrefs. These are user-friendly tools that will crawl your entire website and generate a report on the technical SEO issues that it finds.
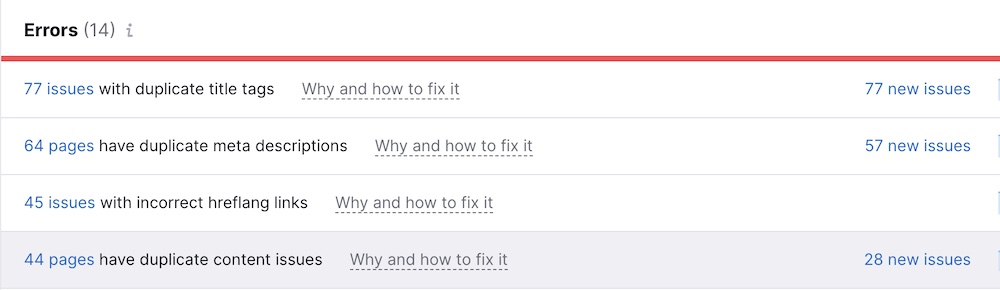
Typically, if you have duplicate content SEO issues, a crawl report will look similar to the one below.
Even though it’s called duplicate content, title tags and meta descriptions also fall under that umbrella. For example, if I were fixing the site from the above audit, I wouldn’t consider duplicate content issues resolved until all instances—including title tags and meta descriptions—are gone.
Auditing tools can help you identify SEO errors, but they have limitations. They may tell you where duplicate content appears but you have to understand how to fix it, which requires technical SEO knowledge.
In addition, if you are using Shopify, I’ve actually seen Semrush miss duplicate content issues in its audits. So, I advise either consulting a technical SEO agency or running a second crawl with another crawling tool like Screaming Frog, and comparing the results.
4 common duplicate content examples
Technical SEO issues vary from site to site. The duplicate content issues may be unique to your site, but they tend to fall into one of these categories.
1. Ecommerce product pages
A common example of duplicate content happens with ecommerce product pages, specifically when you have the same product but different sizes or colors.
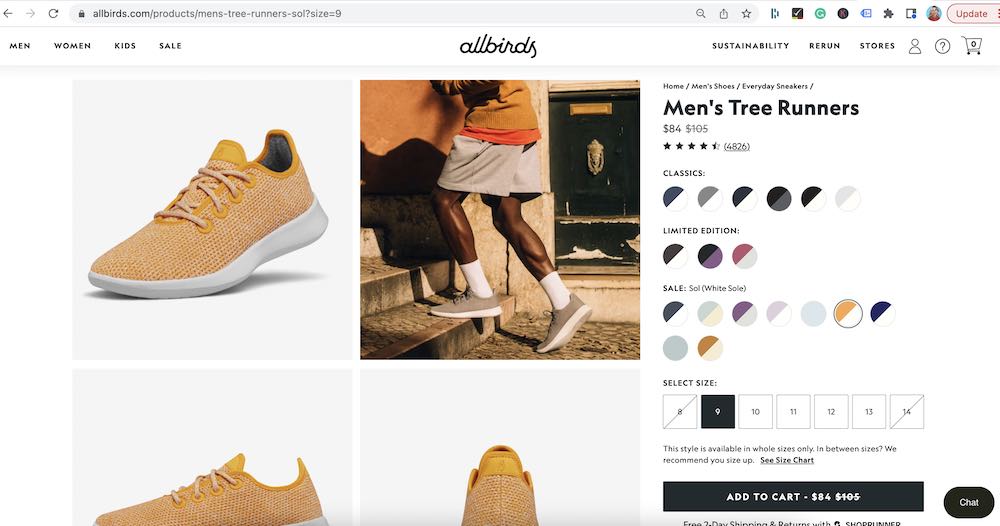
Let’s look at an example. If you go to the Allbirds site and click on the popular tree runner shoe, there are lots of color options and different sizes.
If you choose the “Sol” edition and a size 9, the URL updates to the below.
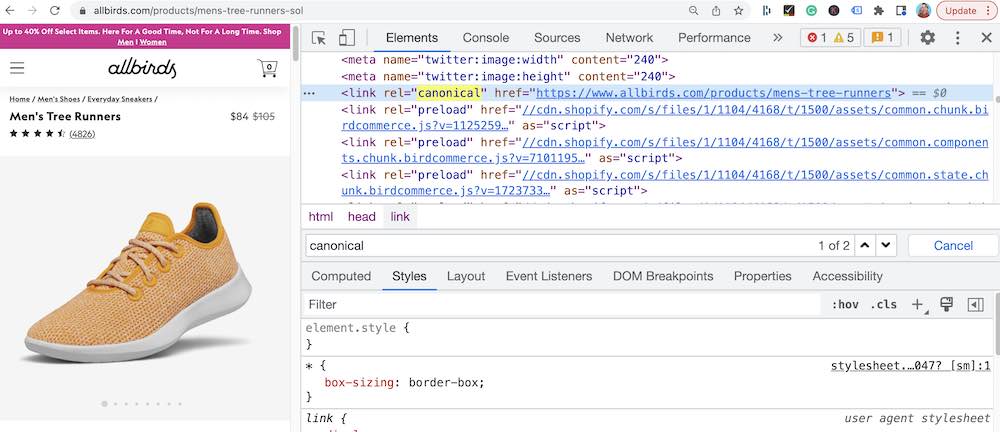
Technically, it could be flagged as duplicate, but it isn’t because they’ve set up a canonical tag. If you look at the image below, you’ll see this line of code below.
- <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.allbirds.com/products/mens-tree-runners”>
It’s a canonical tag, and it signals to Google that the “Sol” URL is a variation and identifies the original URL “mens-tree-runners” as the one to index.
Canonical tags are one way to fix duplicate product pages, but it’s not the only solution.
2. Inconsistent URL structures
If a site has recently gone through a migration or redesign, it is not uncommon to see inconsistent URL structures, specifically in the domain. However, they shouldn’t be there. The best practice is to keep your URL structures consistent across your site.
For example, the Tuff website’s homepage (https://tuffgrowth.com/) uses https and a non-www in the URL. Every other page of the site follows the same structure.
- Resources – https://tuffgrowth.com/growth-marketing-resources/
- Blog – https://tuffgrowth.com/blog/
You get the idea. If your site has varying URL structures it will also result in duplicate content issues. Variations that you might come across include:
- Http or https (you should always have https for security and SEO)
- Www or non-www
- Trailing and non-trailing slashes (slashes at the end of a URL)
Even though it may seem like a slight variation of the URL, Google will view them as two separate pages with the same content. Typically, you’d set up 301 redirects (more on those below) to the URLs with the format that you are using and stay consistent.
3. Duplicate content and global SEO
If your company operates in different countries and you have different sites for each, you’ve likely considered what that means for global SEO.
Luckily, if one site is in the United States and written American English, and another is in Spain and written in Spanish, the pages aren’t usually flagged for duplicate content. Because it is written in two different languages, Google considers them unique.
However, this gets trickier as you move between countries that have similar languages with small adjustments. For example, a site with American English and British English. Without diving too deeply into the nuances of global SEO and hreflang tags, you could get around this by creating unique content for each market.
4. Tracking parameters
When you use tracking parameters, whether they are URL parameters, session IDs, or tracking IDs, it can create duplicate content issues. These URLs may look like this:
- https://example.com/folder/?utm_source
But, they may also have variations like the examples below.
- /?tab_id=
- /?_ga=
- /?session_id=
Primarily, you’ll want to look for the URLs that have a slash (/) followed by a (?). There are ways to get around URL tracking parameters. To fix duplicate content, however, you could use a no-index tag or directive in your robots.txt file.
It will be a line of code that follows a similar format to this:
- Disallow: */?
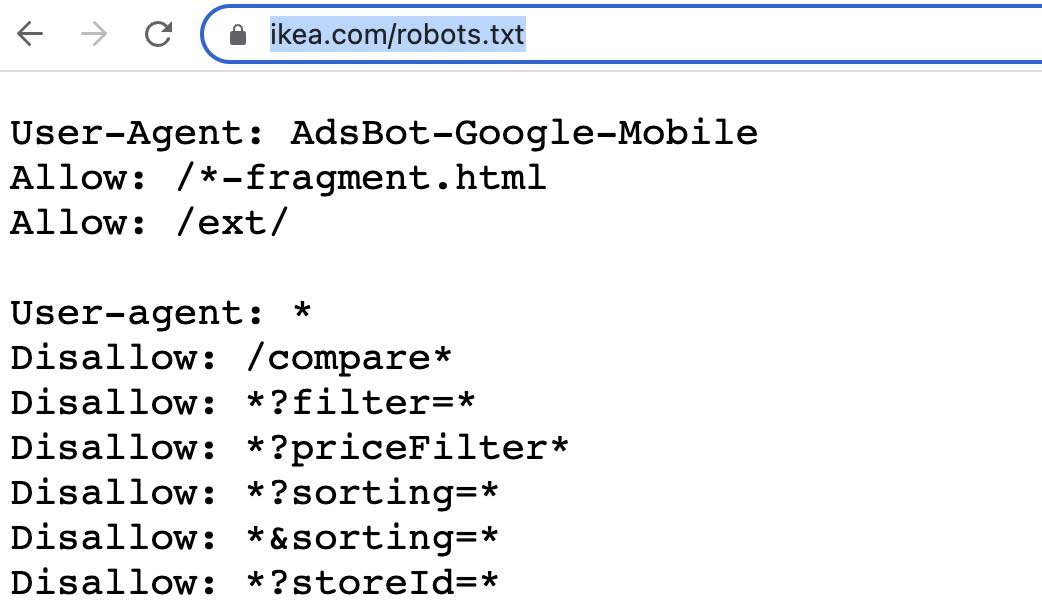
This acts as a suggestion to Google, where you are asking it not to crawl the URLs that follow this URL format. For example, if you go to IKEA’s robots.txt file, they have several disallow directives. Some of these are for filters and others are for tracking parameters.
This is not a comprehensive list of duplicate content examples. Ultimately, you’ll want to conduct a technical SEO audit of your site or hire a technical SEO agency. If you do an SEO audit of your own, it will identify where the errors appear, but it won’t tell you how to fix them or implement the fixes for you.
A technical SEO agency can fix most duplicate content issues, depending on the CMS that you use. If you are on a traditional CMS like WordPress, a technical SEO specialist can fix duplicate content issues in a few clicks.
On the other hand, if you are using a custom, headless CMS like Contentful and Sanity, it takes longer. This is because everything is custom-coded, and as a result, it requires development. You may work with your in-house development team to make fixes with SEO guidance or hire a developer that has an SEO background.
How to fix duplicate content
The solution to fixing duplicate content will depend on why the issue is happening, but generally, there are three technical adjustments that can fix it.
1. 301 redirects
You use 301 redirects to signal to Google that the old URL is no longer in use and specify a new URL that it should point to. Keep in mind that this is a permanent redirect, and you’ll use 301s for more than just fixing duplicate content. If you use a 301 redirect, the old URL should be one that you don’t plan on using again, likely a 404 or broken link.
How to set up a 301 redirect depends on the CMS. For example, if you use WordPress and Yoast Premium, it’s simple. You go to Yoast SEO > Redirects. Then add the URL slugs—the part that appears after the .com slash—in the old and new URL sections. Otherwise, you might directly edit the .htaccess file, which configures your site. Again, this varies by CMS.
2. Canonical tags (rel=”canonical”)
As a reminder, the canonical tag is used to identify one URL as the original. By using it, you can avoid duplicates that have the same or similar content on different URLs.
- <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/” >
First, you need to identify which URL to mark as the canonical one. Then, you add a canonical tag to the head of your HTML code for each of the duplicates.
3. No indexing
Similar to canonical tags, you can ask search engines not to index pages by adding a noindex tag. It looks like this:
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
As the name suggests, it tells search engines that they shouldn’t index—crawl and show the page in search results. For example, if you are running paid ads with landing pages that look similar, you might no-index them to avoid duplicate content and other technical SEO issues.
This list is not comprehensive, but each site is unique. To fix duplicate content issues, you first need to identify and diagnose the problem. Then, look at your site structure and CMS to determine the best course of action. It can get pretty technical depending on the error, so if you’re unsure it’s best to consult a technical SEO specialist or agency.